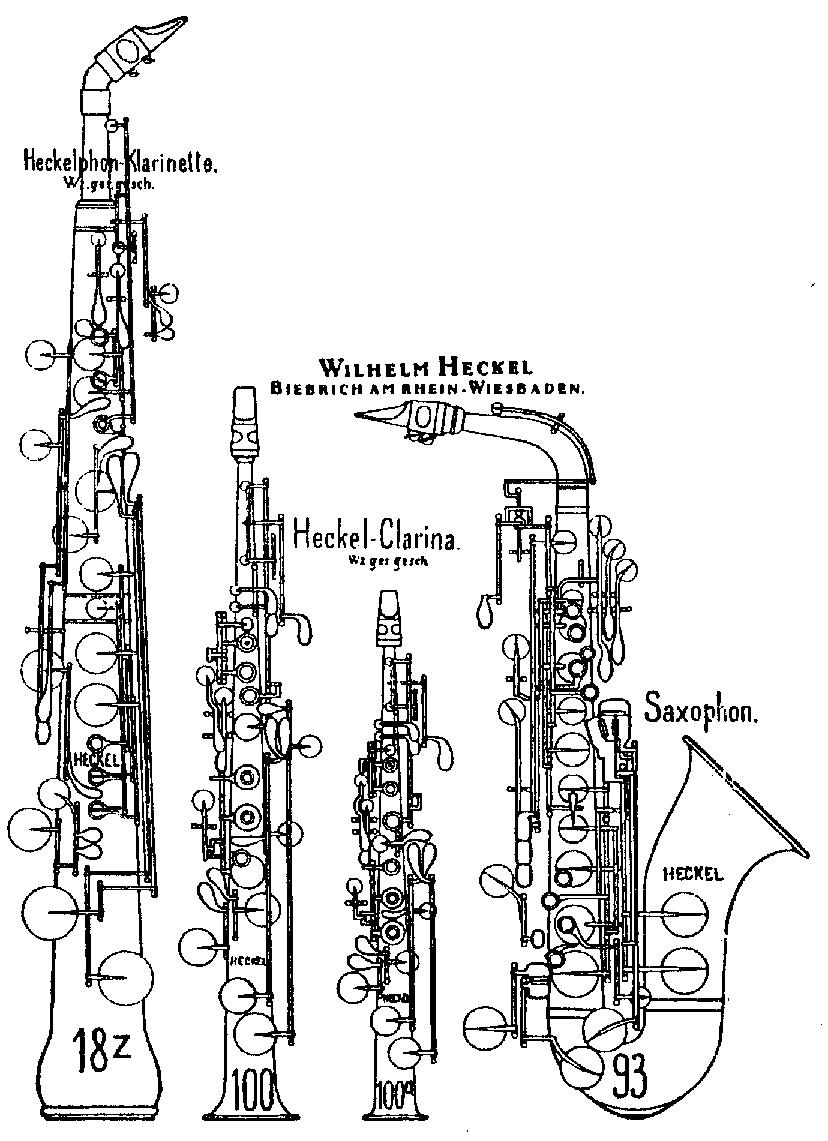
The heckel-clarina, also known as clarina or patent clarina, is a very rare woodwind instrument, invented and manufactured by Wilhelm Heckel in Wiesbaden-Biebrich, Germany. Heckel received a patent for the instrument on 8 December 1889. It was apparently intended to be used for the shepherd’s pipe solo in Act III of Wagner's Tristan und Isolde. It was used beginning in 1891 at the Festspielhaus, Bayreuth as a substitute for Wagner's Holztrompete; the clarina was found more practical and more effective in producing the desired tone-colour.
| Attributes | Values |
|---|
| rdf:type
| |
| rdfs:label
| - Heckel-Clarina (de)
- Heckel-clarina (en)
|
| rdfs:comment
| - The heckel-clarina, also known as clarina or patent clarina, is a very rare woodwind instrument, invented and manufactured by Wilhelm Heckel in Wiesbaden-Biebrich, Germany. Heckel received a patent for the instrument on 8 December 1889. It was apparently intended to be used for the shepherd’s pipe solo in Act III of Wagner's Tristan und Isolde. It was used beginning in 1891 at the Festspielhaus, Bayreuth as a substitute for Wagner's Holztrompete; the clarina was found more practical and more effective in producing the desired tone-colour. (en)
- Die Heckel-Clarina oder Clarina ist ein seltenes Holzblasinstrument, das von Wilhelm Heckel und seinem Sohn Wilhelm Hermann Heckel in Wiesbaden-Biebrich entwickelt und hergestellt wurde. Wilhelm Heckel erhielt am 8. Dezember 1889 ein Patent für das Instrument. Es war anscheinend für die Verwendung in Richard Wagners „Fröhlicher Hirtenweise“ im 3. Akt von Tristan und Isolde vorgesehen. Ab 1891 wurde die Heckel-Clarina im Festspielhaus Bayreuth als Ersatz für die Holztrompete verwendet. Die Clarina wurde als geeigneter zur Produktion der erwünschten Klangfarbe angesehen. (de)
|
| foaf:depiction
| |
| dcterms:subject
| |
| Wikipage page ID
| |
| Wikipage revision ID
| |
| Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage
| |
| Link from a Wikipage to an external page
| |
| sameAs
| |
| dbp:wikiPageUsesTemplate
| |
| thumbnail
| |
| has abstract
| - Die Heckel-Clarina oder Clarina ist ein seltenes Holzblasinstrument, das von Wilhelm Heckel und seinem Sohn Wilhelm Hermann Heckel in Wiesbaden-Biebrich entwickelt und hergestellt wurde. Wilhelm Heckel erhielt am 8. Dezember 1889 ein Patent für das Instrument. Es war anscheinend für die Verwendung in Richard Wagners „Fröhlicher Hirtenweise“ im 3. Akt von Tristan und Isolde vorgesehen. Ab 1891 wurde die Heckel-Clarina im Festspielhaus Bayreuth als Ersatz für die Holztrompete verwendet. Die Clarina wurde als geeigneter zur Produktion der erwünschten Klangfarbe angesehen. Die Heckel-Clarina ist ein Einfachrohrblattinstrument aus Metall mit konischem Verlauf der Schallröhre, das einem Sopransaxophon ähnelt.Es verwendet das Griffsystem der Oboe und das Einfachrohrblattmundstück der Klarinette. Die Heckel-Clarina wurde in B und in Es gebaut. Laut der Werbung ähnelt ihr Klang im unteren Register dem des Englischhorns, dem des Saxophons im mittleren und dem der Klarinette im oberen Register. Das Instrument sollte nicht verwechselt werden mit der , ebenfalls einem seltenen Einfachrohrblattinstrument mit konischem Verlauf der Schallröhre, das jedoch aus Holz besteht und tiefer ist. (de)
- The heckel-clarina, also known as clarina or patent clarina, is a very rare woodwind instrument, invented and manufactured by Wilhelm Heckel in Wiesbaden-Biebrich, Germany. Heckel received a patent for the instrument on 8 December 1889. It was apparently intended to be used for the shepherd’s pipe solo in Act III of Wagner's Tristan und Isolde. It was used beginning in 1891 at the Festspielhaus, Bayreuth as a substitute for Wagner's Holztrompete; the clarina was found more practical and more effective in producing the desired tone-colour. The heckel-clarina is a single reed, conical bore instrument made of metal, resembling a soprano saxophone.It has the fingering of the oboe and a clarinet-type single-reed mouthpiece. Two versions were available: a sopranino in E-flat and a soprano in B-flat. According to Heckel's promotional materials, the heckel-clarina's tone resembled that of a cor anglais in its low register, a saxophone in the middle, and a clarinet in its upper range. The compass of the B♭ instrument is: The clarina was found very effective as a solo instrument. The instrument is not to be confused with the heckelphone-clarinet, also a very rare conical bore single reed woodwind by Heckel but lower in pitch and made of wood. (en)
|
| prov:wasDerivedFrom
| |
| page length (characters) of wiki page
| |
| foaf:isPrimaryTopicOf
| |
| is Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage
of | |
| is foaf:primaryTopic
of | |

![http://dbpedia.demo.openlinksw.com/describe/?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org%2Fresource%2FHeckel-clarina&invfp=IFP_OFF&sas=SAME_AS_OFF]()



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)





![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png)
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png)
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png)