| rdfs:comment
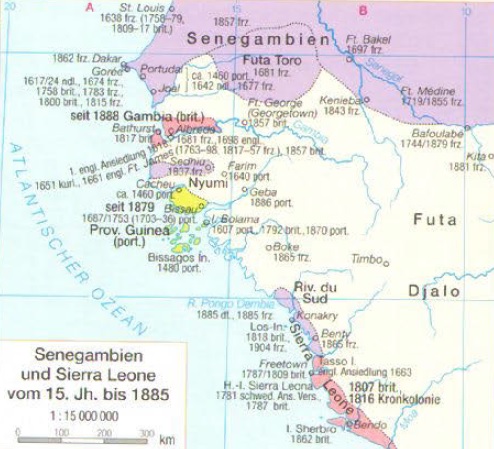
| - Kapitaï und Koba (früher auch Kabitai und Coba oder Kobah) waren zwei westafrikanische Küstenländer, die ab 1884 ein Ziel deutscher Kolonialbestrebungen waren. Trotz eines kaiserlichen Schutzbriefs gab Deutschland seine Ansprüche schon 1885 zugunsten Frankreichs auf. Obwohl die beiden Länder zwischen den Flüssen Rio Pongo und und somit südlich von Senegal und Gambia auf dem Gebiet des heutigen Guinea lagen, wurden sie im Sprachgebrauch des 19. Jahrhunderts dem geografischen Raum Senegambien zugerechnet. Die kurzlebige deutsche Besitzung wurde vereinzelt auch Dembiah-Kolonie oder nach ihrem Begründer Colinsland genannt. (de)
- Kapitaï and Koba (also known as Kabitai and Coba or Kobah) were two areas on the coast of West Africa which were the object of German colonial initiatives in 1884 and 1885. They lay between the Pongo and Dubréka rivers, south of Senegal and Gambia in modern Guinea; in the terms commonly used in the 19th century they were considered part of Senegambia. The short-lived German colony there was known as the Dembiah colony or Colinsland (after its founder). (en)
- Kapitaï y Koba (también conocidas como Kabitai y Coba o Kobah) fueron dos áreas en la costa de África occidental que fueron objeto de iniciativas coloniales alemanas en 1884 y 1885. Se encuentran entre los ríos Pongo y Dubréka, al sur de Senegal, y Gambia en la Guinea moderna; en los términos comúnmente utilizados en el siglo XIX, se consideraban parte de Senegambia. La colonia alemana, de corta duración, era conocida como colonia Dembiah o Colinslandia (nombrada así por su fundador). (es)
- L'homme d'affaires de Stuttgart (de) faisait du commerce en Afrique de l'Ouest depuis 1870 pour le compte d'une société française. En 1882, la France a revendiqué la région comme faisant partie de son territoire des Rivières du Sud, bien qu'elle n'ait pas agi pour obtenir un contrôle effectif. À la suite de cette réclamation, Colin s'est séparé de ses partenaires français et a créé sa propre entreprise, bien que le (de) refusé de lui apporter un quelconque soutien. (fr)
|
| has abstract
| - Kapitaï und Koba (früher auch Kabitai und Coba oder Kobah) waren zwei westafrikanische Küstenländer, die ab 1884 ein Ziel deutscher Kolonialbestrebungen waren. Trotz eines kaiserlichen Schutzbriefs gab Deutschland seine Ansprüche schon 1885 zugunsten Frankreichs auf. Obwohl die beiden Länder zwischen den Flüssen Rio Pongo und und somit südlich von Senegal und Gambia auf dem Gebiet des heutigen Guinea lagen, wurden sie im Sprachgebrauch des 19. Jahrhunderts dem geografischen Raum Senegambien zugerechnet. Die kurzlebige deutsche Besitzung wurde vereinzelt auch Dembiah-Kolonie oder nach ihrem Begründer Colinsland genannt. (de)
- Kapitaï and Koba (also known as Kabitai and Coba or Kobah) were two areas on the coast of West Africa which were the object of German colonial initiatives in 1884 and 1885. They lay between the Pongo and Dubréka rivers, south of Senegal and Gambia in modern Guinea; in the terms commonly used in the 19th century they were considered part of Senegambia. The short-lived German colony there was known as the Dembiah colony or Colinsland (after its founder). (en)
- Kapitaï y Koba (también conocidas como Kabitai y Coba o Kobah) fueron dos áreas en la costa de África occidental que fueron objeto de iniciativas coloniales alemanas en 1884 y 1885. Se encuentran entre los ríos Pongo y Dubréka, al sur de Senegal, y Gambia en la Guinea moderna; en los términos comúnmente utilizados en el siglo XIX, se consideraban parte de Senegambia. La colonia alemana, de corta duración, era conocida como colonia Dembiah o Colinslandia (nombrada así por su fundador). (es)
- L'homme d'affaires de Stuttgart (de) faisait du commerce en Afrique de l'Ouest depuis 1870 pour le compte d'une société française. En 1882, la France a revendiqué la région comme faisant partie de son territoire des Rivières du Sud, bien qu'elle n'ait pas agi pour obtenir un contrôle effectif. À la suite de cette réclamation, Colin s'est séparé de ses partenaires français et a créé sa propre entreprise, bien que le (de) refusé de lui apporter un quelconque soutien. En 1883 et 1884, avec le soutien de son frère Ludwig, directeur de la Württembergische Vereinsbank à Stuttgart, Colin établit ses propres comptoirs commerciaux dans les zones non réclamées de Baga et Sousou et le long de la rivière Dubreka, notamment un à Bouramayah et signé des accords avec les dirigeants locaux. Dans la même région, il y avait aussi un poste de traite français et un poste britannique, avec des employés allemands. Lors d'une réunion du chancelier Otto von Bismarck avec des hommes d'affaires faisant du commerce en Afrique le 28 avril 1884, Colin a d'abord demandé au gouvernement de protéger ses possessions en annexant le territoire des Rivières du Sud. Le 9 mars 1885, avec des associés de Hambourg, Colin fonda la société Fr. Colin, Deutsch-Afrikanisches Geschäft à Francfort-sur-le-Main, pour explorer et développer le commerce avec l'Afrique de l'Ouest et notamment pour atteindre la source du Niger dans les montagnes du Fouta Djallon.. Le capital fondateur était de 600 000 marc dont 420 000 marc étaient directement souscrits à Francfort, avec des actions d'une valeur nominale de 10 000 marc. Les comptoirs commerciaux de Colin en Afrique furent rattachés à la nouvelle société. Grâce à son frère, Colin a pu s'associer en tant que partenaires et sponsors, le prince Hermann zu Hohenlohe-Langenburg, comte (de), Freiherr (de), les banquiers (de) et (de), ainsi que les hommes d' affaires (de), (de), (de) et (de). Ces noms lui assuraient la bonne volonté du Foreign Office. (fr)
|

![http://dbpedia.demo.openlinksw.com/describe/?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org%2Fresource%2FKapitaï_and_Koba&invfp=IFP_OFF&sas=SAME_AS_OFF]()



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)





_Jean-Marie_Bayol_and_William_Fernandez.jpg)
.jpg)


_Jean-Marie_Bayol_and_William_Fernandez.jpg)


.jpg)

![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png)
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png)
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png)