A terminal node controller (TNC) is a device used by amateur radio operators to participate in AX.25 packet radio networks. It is similar in function to the Packet Assembler/Disassemblers used on X.25 networks, with the addition of a modem to convert baseband digital signals to audio tones. The first TNC, the VADCG board, was originally developed by Doug Lockhart, VE7APU, of Vancouver, British Columbia.
| Attributes | Values |
|---|
| rdf:type
| |
| rdfs:label
| - Terminal Node Controller (de)
- Terminal Node Controller (fr)
- Terminal node controller (en)
|
| rdfs:comment
| - Als Terminal Node Controller (TNC) bezeichnet man ein Modem für den Packet-Radio-Betrieb im Amateurfunk. Er stellt die Verbindung zwischen Rechner und Funkgerät her und wird mit der seriellen Schnittstelle oder parallelen Schnittstelle und dem Mikrofon- und Lautsprecheranschluss des Funkgeräts verbunden. Darüber hinaus ist noch eine Betriebsspannung notwendig, meist über einen Stecker zugeführte Gleichspannung, in Ausnahmefällen wie beim TNC1 auch direkt die Netzwechselspannung. (de)
- Un Terminal Node Controller (TNC) est un appareil utilisé par les radioamateurs pour se connecter à des réseaux packet radio AX.25. Cet appareil reprend les fonctions des (PAD) des réseaux X.25, et leur ajoute un modem chargé de la conversion entre signaux numériques et signaux audio. Le premier TNC a été développé par Doug Lockhart, VE7APU, de Vancouver, et diffusé via le groupe Tucson Amateur Packet Radio et les modèles TNC-1 et TNC-2. (fr)
- A terminal node controller (TNC) is a device used by amateur radio operators to participate in AX.25 packet radio networks. It is similar in function to the Packet Assembler/Disassemblers used on X.25 networks, with the addition of a modem to convert baseband digital signals to audio tones. The first TNC, the VADCG board, was originally developed by Doug Lockhart, VE7APU, of Vancouver, British Columbia. (en)
|
| foaf:depiction
| |
| dcterms:subject
| |
| Wikipage page ID
| |
| Wikipage revision ID
| |
| Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage
| |
| Link from a Wikipage to an external page
| |
| sameAs
| |
| dbp:wikiPageUsesTemplate
| |
| thumbnail
| |
| has abstract
| - Als Terminal Node Controller (TNC) bezeichnet man ein Modem für den Packet-Radio-Betrieb im Amateurfunk. Er stellt die Verbindung zwischen Rechner und Funkgerät her und wird mit der seriellen Schnittstelle oder parallelen Schnittstelle und dem Mikrofon- und Lautsprecheranschluss des Funkgeräts verbunden. Darüber hinaus ist noch eine Betriebsspannung notwendig, meist über einen Stecker zugeführte Gleichspannung, in Ausnahmefällen wie beim TNC1 auch direkt die Netzwechselspannung. (de)
- Un Terminal Node Controller (TNC) est un appareil utilisé par les radioamateurs pour se connecter à des réseaux packet radio AX.25. Cet appareil reprend les fonctions des (PAD) des réseaux X.25, et leur ajoute un modem chargé de la conversion entre signaux numériques et signaux audio. Le premier TNC a été développé par Doug Lockhart, VE7APU, de Vancouver, et diffusé via le groupe Tucson Amateur Packet Radio et les modèles TNC-1 et TNC-2. (fr)
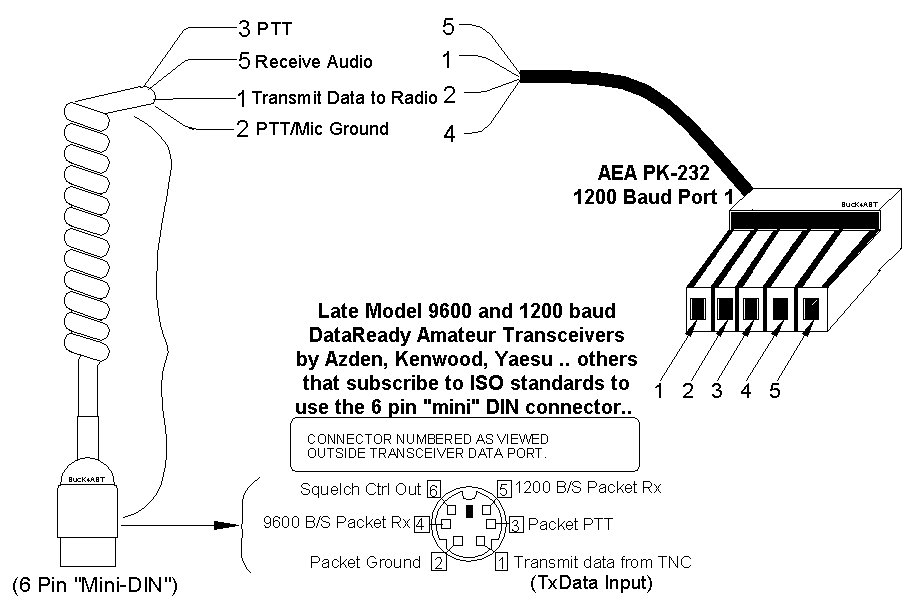
- A terminal node controller (TNC) is a device used by amateur radio operators to participate in AX.25 packet radio networks. It is similar in function to the Packet Assembler/Disassemblers used on X.25 networks, with the addition of a modem to convert baseband digital signals to audio tones. The first TNC, the VADCG board, was originally developed by Doug Lockhart, VE7APU, of Vancouver, British Columbia. Amateur Radio TNCs were first developed in 1978 in Canada by the Montreal Amateur Radio Club and the Vancouver Area Digital Communications group. These never gained much popularity because only a bare printed circuit board was made available and builders had to gather up a large number of components. In 1983, the Tucson Amateur Packet Radio (TAPR) association produced complete kits for their TNC-1 design. This was later available as the Heathkit HD-4040. A few years later, the improved TNC-2 became available, and it was licensed to commercial manufacturers such as MFJ. In 1986, the improved "TNC+" was designed to run programs and protocols developed for the original TNC board.TNC+ also included an assembler and a version of Forth (STOIC), which runs on the TNC+ itself, to support developing new programs and protocols. (en)
|
| gold:hypernym
| |
| prov:wasDerivedFrom
| |
| page length (characters) of wiki page
| |
| foaf:isPrimaryTopicOf
| |
| is Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage
of | |
| is Wikipage redirect
of | |
| is Wikipage disambiguates
of | |

![http://dbpedia.demo.openlinksw.com/describe/?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org%2Fresource%2FTerminal_node_controller]()



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)



![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)





![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png)
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png)
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png)